Advancements in healthcare and our understanding of how the body works are happening all the time, especially as our use of technology alongside human knowledge and treatment grows. Not only is this technology making a difference in how people are cared for in medical institutions, but it’s also giving individuals access to more data about their personal health and wellbeing and allowing them to notice symptoms and manage conditions independently.
At KO2, our work in the embedded systems and electronics sector means that we see plenty of candidates placed in roles in the healthcare industry, particularly on projects or with companies developing medical devices. It’s an area that has been growing for some time and has the potential for a lot of really impactful innovation, with many of our current clients and candidates seeking guidance on navigating these new developments.
In this article, we share some of the most interesting examples of how embedded systems and AI technology are transforming healthcare, helping candidates and employers in this industry keep on top of the latest development and predictions.
Embedded Systems in Healthcare
Embedded systems technology is used in healthcare for all kinds of purposes, both as part of standardised medical machinery and for personal use. Being able to connect devices and quickly monitor data in real-time is useful in a wide range of medical scenarios, and whilst this kind of technology can’t perform particularly complex tasks, it can manage processes that can save healthcare staff a lot of time.
Here are some of the key ways that embedded systems have been having an impact on technology in healthcare.
Defibrillators
A classic example of how embedded systems have been used in medical devices is a defibrillator. These devices are used by medical professionals and sometimes members of the public in emergencies to treat people who are experiencing life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, or heart attacks.
Defibrillators use embedded systems technology to monitor a person’s heartbeat and detect whether it is irregular. If so, it will analyse if and when to deliver an electrical shock to the heart and do this so that the heartbeat hopefully returns to normal. These devices have been incredibly impactful in improving the effectiveness of first aid given to people that have suffered from cardiac arrest and are a great example of how embedded systems can create life-saving devices that are very simple to use.

Remote Monitoring
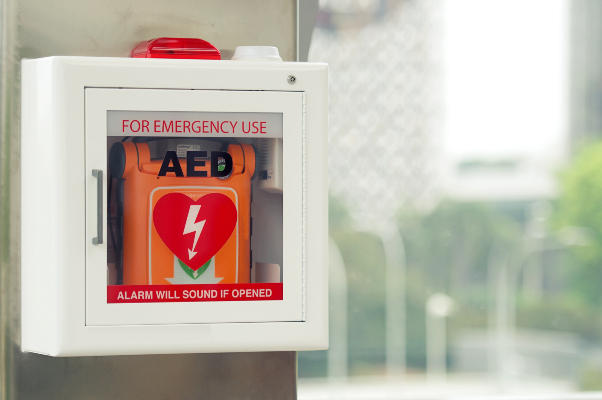
One issue faced by the healthcare industry at the moment is a lack of space inside institutions for all the patients that need care. When a patient is physically well enough to care for themselves, but needs to be regularly monitored to keep an eye on their condition, embedded systems devices allow for remote monitoring which can free up hospital beds and ensure that patient safety isn’t compromised when they are sent home.
With this kind of technology, a patient may be fitted with a device that records data about a range of functions like heartbeat, oxygen or glucose levels and quality of sleep. This data is shared on a system that a doctor can access, allowing them to keep an eye on a patient’s condition and be notified if something goes wrong.
Patients with long-term health conditions can also be monitored remotely, which minimises the number of in-person appointments they need to attend for tests. Instead, medical staff can keep an eye on their condition and arrange an appointment if anything starts to look worrying.
Remote monitoring can also be done in hospitals to reduce round-the-clock monitoring that requires nurses to sit with patients overnight, freeing up medical staff whilst ensuring that they can act quickly if needed.
Personal Condition Monitoring
Along with giving medical staff the ability to monitor their patient’s conditions remotely, embedded systems technology allows patients with long-term health problems to manage their own symptoms and conditions. This minimises the amount of professional intervention and care needed and can also allow them to have a better quality of life.
An example of embedded systems used in this way is a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) which is given to patients with diabetes. A tiny sensor is embedded in a diabetic person’s skin and continuously tracks the glucose in their blood, sharing this data with a mobile app. This allows for glucose monitoring without having to prick the skin, and means that glucose pumps or injectors can be used more effectively and a diabetic person can be made aware of any dangerous changes in their blood sugar.
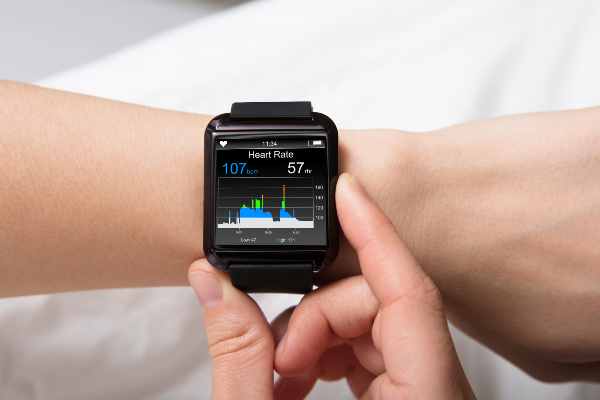
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices have become incredibly popular in recent years, beginning with the popularity of smartwatches and developing into all kinds of other wearables that allow the user to keep track of different vitals. These are regularly used by athletes and people wanting a more comprehensive look at their physical fitness, but can also be used to track things like sleep quality, fertility and heart health.
Whilst the accuracy of these devices isn’t often of the same quality as medical monitoring systems, they can help with the early identification of health conditions and allow people to feel more in control of their health and wellbeing.

Infection Control
Finally, one potential application of embedded systems medical tech is to help with infection control, which has been a particularly relevant issue since the events of the COVID-19 pandemic. When social distancing was an essential part of trying to reduce the spread of the virus, embedded systems technology was proposed that measured your proximity to others or the number of people in a space and provided a warning.
The spread of coronavirus now no longer poses the same serious threat, but infectious diseases are still a reality that societies are faced with, which means that this kind of technology may be developed again in the near future.
The Rise of AI Medical Devices and Machines
Artificial Intelligence seems to be having a heyday at the moment as more and more software becomes available to the general public, but this kind of technology has been around for over a decade now and was already being used in industries like healthcare. Here are some examples.
Analysis and Diagnosis
AI is beginning to be used to optimise the analysis of patient tests and scans to make diagnosis more effective and help to speed up the time taken between being diagnosed and treated for a health condition. Some AI models are being trained to analyse scans like mammograms and detect the presence of breast cancer without the need for a biopsy, which makes early intervention easier. Others are being trained to learn the early symptoms of heart disease that can be present in things like blood tests and help doctors prevent more severe cases from developing.
Medicine Development
AI is also being used to help make the development of new medicines faster, reducing the need for a lot of testing and refining by running simulations or training programs to identify more effective approaches faster than a human could. There’s also the potential to use AI systems to analyse existing medicine and develop this to treat other conditions or work more efficiently, which could lead to significant improvements in mortality rates and recovery times.
Medical Robots
An application of AI technology that has been talked about a lot in the healthcare industry is the use of artificial intelligence to make medical robots more effective. A range of institutions have started to use robotics in things like surgery to make the work of humans more effective, but with AI these robots will be able to perform more complex procedures and potentially remove the need for human surgeons in certain cases, creating more accessible treatment and reducing the problems caused by only have a small number of specialists in an area of medicine.
How Will This Technology Transform Healthcare in the Future?
Whether you’re an employer running a business in the health tech sector or an engineer seeking a career in this area, it’s important to have an idea of what the future of technology in healthcare is going to look like. Here are some of the key predictions.
It’s clear that embedded systems and embedded software have a wide range of applications in the healthcare industry, and they will likely be used more and more in the future as this technology is refined. Remote monitoring is already an important area of development, and it’s predicted that more and more devices and systems will be created that allow doctors to monitor their patient’s conditions remotely, identify early signs of deterioration and mean that more patients can spend time at home when they previously would have had to stay in hospital.
Wearables are another area where we’re seeing a lot of interest at the moment, and as consumer demand for these devices grows, it’s likely to be a big focus for development in the future. Already, wearable technology is expanding from watches to other, more compact devices and the monitoring options of these are becoming more accurate and intuitive.
Consumers want more control and insight into their health, and as new devices roll out that grant this insight, companies will also have to consider what other initiatives will be launched to help consumers change habits and improve their vitals. As a result of this, population health has the potential to improve if this kind of technology is accessible to everyone, especially older consumers who are made more aware of their health and how to sustain it.
Embedded systems are an important part of virtual reality technology, which is being used in healthcare as a way to provide more training to medical staff without having to use real patients. There’s the potential for much more teaching to be done using 3D training simulators as the applications of this technology expand, making it possible for more medical professionals to train in complex procedures and gain more practical experience whilst they study.
In terms of AI medical devices and machinery, this technology has the potential to transform healthcare because of how it can improve current diagnostic procedures. Whether this involves training AI to spot signs of disease or conditions, or using it to speed up the diagnosis process, this will increase how quickly patients can be treated and potentially help to catch early symptoms of disease before they become more serious, leading to more effective treatment and great recovery rates.
Finally, using AI to assist with clinical research in the healthcare industry could transform how we treat a wide range of diseases and how quickly we can find treatments or vaccines for new illnesses. AI is unlikely to replace the people that work in this industry sector, but programs and systems could be developed that automate tasks or make it easier to highlight patterns and draw conclusions, helping to optimise the research process.
Summary
New medical technology is being developed all the time, and engineers working in electronics and embedded systems have a range of opportunities when it comes to applying their skills and experience to this sector. Healthcare is an industry that isn’t going anywhere and therefore is a great place to develop your career and work on projects that will make a tangible difference to population health, and we’re seeing plenty of opportunities for engineers in this area at the moment.
If you’re an engineer looking for an opportunity to work with embedded systems and AI in the medical device industry, KO2 is a specialist recruitment partner that can help you find the ideal role. Check out our available positions or get in touch to speak to our team about what you’re looking for.







