Emerging Trends in Automotive Embedded Systems
From Connected Cars to Autonomous Vehicles


From Connected Cars to Autonomous Vehicles
The automotive industry is a sector that is seeing significant development at this moment in time.
With the prospect of diesel and petrol car production being banned from 2030, vehicle electrification is rapidly on the rise. Artificial intelligence technology is coming on in leaps and bounds, with new integrations and applications being announced all the time.
Smart technology is becoming integrated into our daily lives, and now consumers expect their purchases to offer personalised insight and adaptive features that offer more insight and control. And as Industry 4.0 makes its mark on all kinds of technology, the Internet of Things is connecting more and more of our devices and machines, including our vehicles.
With all of the above influencing all kinds of projects and ideas, working in the automotive industry is an exciting place to be for an engineer at the moment. Automotive embedded systems is an area where demand is growing, but alongside all these new opportunities there are also significant challenges for engineers to overcome.
As a specialist recruitment agency in the electronics and embedded systems sector, we see plenty of opportunities for embedded systems engineers to work in the automotive industry. It’s an exciting time to be developing new software and systems for vehicles, and in this article we discuss the current role of embedded systems in the automotive sector, new technology trends in the automotive industry and the current challenges that engineers are facing.

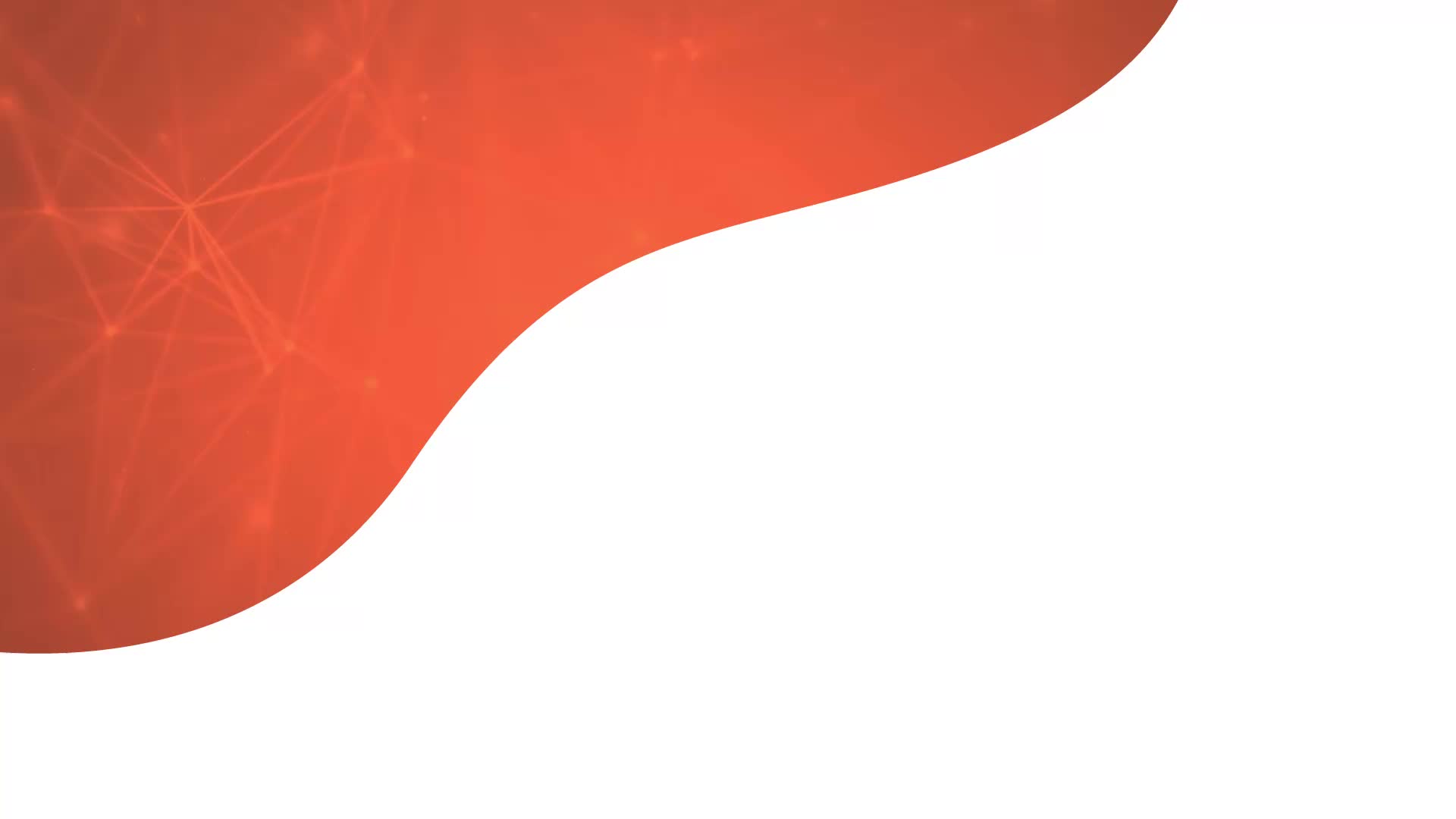
Automotive embedded systems manage functions in a vehicle such as engine performance, navigation, airbag deployment, adaptive cruise control, sensors, parking systems, anti-lock braking system and in-vehicle entertainment. As vehicle technology becomes more advanced, more and more functionalities are controlled by connected systems that ensure that vehicles work more efficiently, issues are spotted quickly and the driver has more control over their experience.
At present, there is a range of different ways that embedded systems are being used in automotive design. A significant contributor to this is the modern consumer’s desire to have more personalised experiences, which embedded systems offer in a car by giving the driver more control over different features and providing data on performance and efficiency.
Many of the systems that most drivers take for granted in their vehicles are actually controlled by embedded systems. Navigation using GPS relies on embedded systems and software, and parking assistance systems use a range of embedded devices all around the car to make it easier for drivers to park safely.
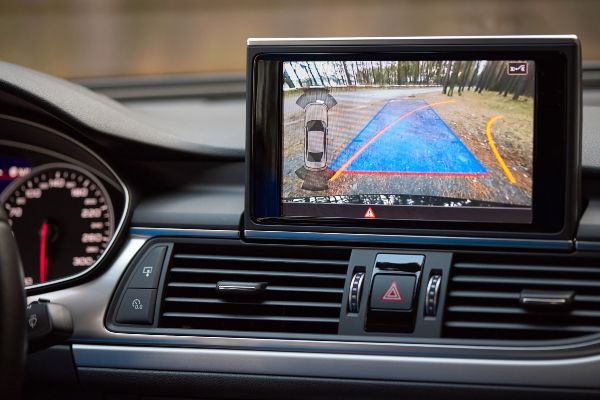
A significant development in automotive technology has been the rise of electric vehicles, driven by the increasing problems of the global climate crisis and the UK government’s pressure to adopt electric technology for automobiles. Embedded systems are a key part of this technology, used in battery management systems, helping to manage the distribution of energy in the vehicle and collecting data about the car and the driver’s performance.
Embedded systems are also used in electric vehicle charging technology, allowing charging points and vehicles to communicate. They allow charging stations to learn how much power a vehicle needs and adapt the charging process depending on the model of the car, allowing for more efficient and optimised charging.
Another use of embedded systems in electric vehicles is that they allow manufacturers of vehicles and charging technology to gather data from charging stations to improve the experience. Technicians are able to identify problems in real-time and deliver faster solutions, and energy providers can track data about peak times and average lengths of charges to be more efficient with their energy delivery.
Automotive embedded systems are a key part of intelligent transport systems, which are appearing in cities around the world to provide better public transport, reduce traffic congestion and help to cut down on emissions. Embedded systems share data with wider traffic systems and help to deliver traffic reports and inform smart traffic instructions that can prevent accidents and reduce traffic jams.
One area where embedded systems play a crucial role in automobile technology is in smart sensors within a vehicle. These allow the driver to have a better understanding of potential hazards all around the car, not just in their line of vision, and be alerted to potential hazards before they might have noticed them independently. Embedded systems also facilitate safer driving with the use of airbag systems and adaptive cruise control.
Embedded systems in automobiles are already responsible for many features that have become commonplace across all kinds of vehicles. But the application of these systems and software is an area that continues to develop, presenting a range of exciting opportunities for those working as embedded systems engineers in the automotive industry.
Electric vehicles aren’t a new development, but they are quickly becoming more mainstream purchases for consumers. With the increase in demand for this technology comes the need for better infrastructure for electric vehicles and the amount of charging that they need.
Increasing the time a vehicle takes to charge is a key focus, which embedded systems can help with by providing real-time data to help adapt the charging process to increase efficiency. As the number of charging stations grows, there’s also the potential for this technology to allow drivers to see nearby chargers and check availability, helping reduce waiting times and make it easier to plan journeys.
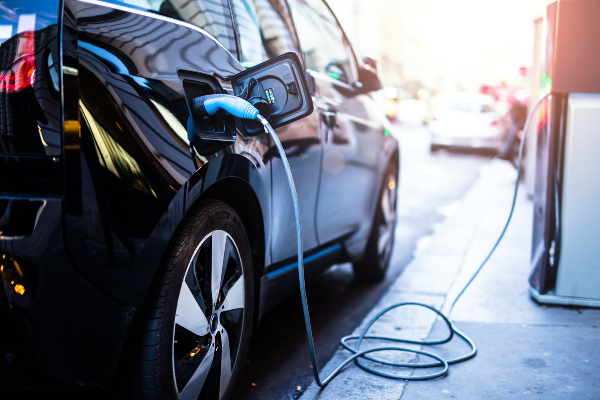

AI technology has an ever-growing list of applications, and in the automotive industry it can work in tandem with embedded software to help enable safer driving. A current example of this involves headlights that automatically dim when another vehicle approaches, but there’s a huge range of potential when it comes to the kind of data that embedded systems can connect and then the suggestions and improvements to the driving experience that AI can make based on this data.
Speaking of safer driving, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are an area of automobile technology where embedded systems have a lot of potential. Sensors and software allow vehicles to do everything from ‘reading’ traffic signs to performing emergency stops, and as this technology is refined there will be more ways that our vehicles can facilitate safer driving by reacting to hazards and providing intuitive assistance.
ADAS technology is the foundation of fully autonomous vehicles, so embedded systems engineers have the potential to get involved in this groundbreaking new development in the automotive industry. Self-driving cars are only in the early stages of real-life application and have plenty of challenges to overcome to reach perfect use, but embedded systems will be an integral part of this.
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication is the term used to describe how cars communicate wirelessly with one another using embedded systems technology. V2V systems are already used in intelligent transport systems, but they have the potential to help these systems be used across a wider range of locations and vehicles and become an essential part of how people travel by car. When you combine V2V technology with vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, new solutions could emerge regarding traffic control, driver safety and fuel efficiency.

The final area we’re going to highlight because of its potential for embedded system development is ‘smart’ vehicles. We’ve already discussed some of the features of this idea; autonomous driving options, intelligent transport system connectivity and more efficient energy management. But this could be taken further with vehicles that can read a driver’s vitals and make adjustments based on their mood or energy levels, or vehicles that provide suggestions to improve a driver’s safety on the roads, which could affect their car insurance.
Climate change and the increased need for financial efficiency means that many consumers may want their vehicles to be more efficient with how they use fuel and the environmental impact of this. There’s also a lot of potential for ‘smart’ vehicle technology that optimises route suggestions and energy usage based on the driver’s preferences, as well as providing suggestions on how they can be a ‘greener’ driver.
Whilst there are plenty of opportunities to be excited about in terms of the future applications of embedded systems in automobiles, there are also some significant challenges that engineers should be aware of and prepared for.
The first of these is the security of the embedded systems and networks being used in automotive technology. Increased connectivity leads to increased chances of networks being hacked and either manipulated or having important data stolen. Alongside the development of new automotive embedded systems comes the necessity of new safety standards and more vigorous testing procedures to ensure that drivers aren’t being put at risk.
Speaking of risk, there is a higher level of consumer safety to consider when developing embedded software for vehicles. You may already be aware of how initial tests of autonomous vehicles are showing that malfunctioning technology can have a severe impact on passenger safety, and there are similar risks when you’re creating new functions that give vehicles more control.
Not only do you risk the safety of the driver and their passengers if something goes wrong in a vehicle, but you also risk other road users and passers-by as well. The consumer safety stakes are very high in the automotive industry, and this may present roadblocks and setbacks when you’re trying to introduce new technologies or ensure that a new system is safe.
A final challenge faced by automotive embedded systems engineers is that it can be harder to roll out updates or successfully debug systems. The more devices that are connected in a network, the more devices and systems that are impacted when something goes wrong, and the harder it can be to find a solution. It’s also well known that trying to update devices that are connected by the Internet of Things, making updating software and firmware across a large number of vehicles a significant challenge.

Technology trends in the automotive industry present a lot of very exciting possibilities, especially if you’re an embedded systems engineer. Not only is there the potential to make vehicles that are much safer to use and better for the environment, but intuitive technology and smart systems can also gather more data to deliver better instructions to drivers on everything from how they’re driving to the route they should take. And as 2030 and total vehicle electrification draws closer, there are plenty of ways that embedded technology will be needed to assist with necessary infrastructure and improved user experience.
If you’re an embedded systems software engineer looking for a role in the automotive industry, KO2 is a specialist recruitment agency that knows this sector inside out. Take a look at our current job opportunities or get in touch for more advice on working with automotive embedded technology.
 Preventing Burnout: The Key to Retaining Software Developers
Preventing Burnout: The Key to Retaining Software Developers